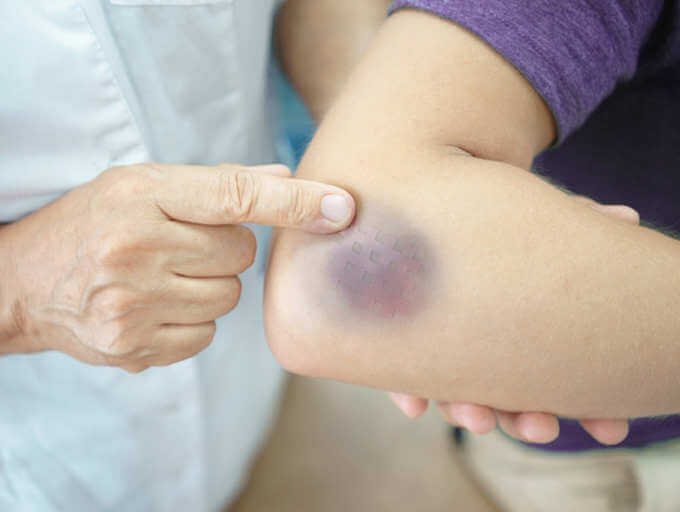
Bruises and Hematoma are medical conditions caused by injuries sustained on the soft tissue of the body. Generally, both conditions result from a series of similar activities; however, these injuries occur at different trauma spots.
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a mild injury to blood vessels that causes blood to leak under the skin. Irritation to the skin causes a red to blue discoloration that fades over time and becomes a light brown color as the blood soaks into the body.
As a medical condition, Hematoma develops from traumatic injuries to blood vessels in the body, which causes blood to clot under the skin, muscles, or internal organs. Hematoma can occur in any part of the body; however, the most fragile hematoma appears in the brain and can lead to a severe medical emergency.
Learning to distinguish both conditions, symptoms, and treatment options can save you and your loved ones from eminent medical complications.
What are the Causes of Hematoma and Bruises?
Bruises and Hematoma are medical conditions resulting from an intense force or physical impact on the body, causing blood to leak from ruptured blood vessels. The Physical implications that might result in breakage of blood vessels leading to bruise and Hematoma include:
- Car accident
- Sport activities
- Fractures
- Medical surgeries
- Abnormal skin compression
What are the Risk Factors of Hematoma and Bruises?
Specific factors that can increase the risk of developing Hematoma and bruise include but are not limited to:
Age
Aging is a significant factor that increases the risk of developing bruises and Hematoma. As a person ages, the skin becomes thinner and fragile, making them prone to minor injuries resulting in bruises or Hematoma.
Medication
Certain medications such as Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), e.g., aspirin, blood thinners like warfarin, heparin, and certain supplements like omega 3-fatty acids, can increase the likelihood of developing Hematoma and bruise.
Underlying health conditions
Underlying health conditions such as vitamin k deficiency, liver disease, cancer, bleeding disorder, e.g., hemophilia, can disrupt normal blood vessel activities, which prevent ruptured vessels from stopping bleeding.
What are the Symptoms of Bruise and Hematoma?
Symptoms of bruises and Hematoma appear to be the only significant difference between both medical conditions. These symptoms can be a minor or life-threatening condition, depending on the location and intensity of the trauma. A few ways to distinguish between bruise and Hematoma include:
Common Symptoms of Bruise
- Mild swelling around trauma location
- Dark blue, black, discoloration
- Tenderness around trauma location
Common Symptoms of Hematoma
Symptoms of Hematoma depend on the size and location of the Hematoma. Common symptoms include:
- Slurred speeches
- Headache
- Seizure
- Unconsciousness
- Inflammation
- Swelling
- Severe pain
- Redness around trauma location
- Other symptoms of Hematoma may include abdominal pain, disorientation, and loss of balance.
How to Diagnose Bruises and Hematoma
Doctors can quickly diagnose superficial bruises and Hematoma during physical examination based on discoloration of the skin. In severe cases of Hematoma, an imaging test like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), x-ray, or a computed tomography (CT) scan may be necessary.
Treatment for Bruise and Hematoma
Generally, bruises resolve and heal on their own, but treatment may hasten recovery and reduce discomfort. Majority of bruises and superficial (surface) hematoma traditional treatment usually involve the R.I.C.E (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) method.
Specifically, the steps of the RICE method include:
- Resting the affected area to minimize inflammation and ease discomfort
- Applying a bag of ice several times a day to the affected area
- Compress the affected region with a bandage for proper reabsorption of blood into the body
- Elevating the affected area can improve adequate blood flow
Severe cases of Hematoma would require a surgical procedure to drain the blood out of the affected area.
When to Visit your Doctor
If you or your loved ones show signs of mild Hematoma after an injury, an over-the-counter pill might be enough to help ease discomfort as this condition will eventually heal on its own.
However, if you experience any form of pain, increased warmth, and redness, call your doctor and seek immediate medical attention to avoid life-threatening complications.